|
Montana Wind
Power Resources 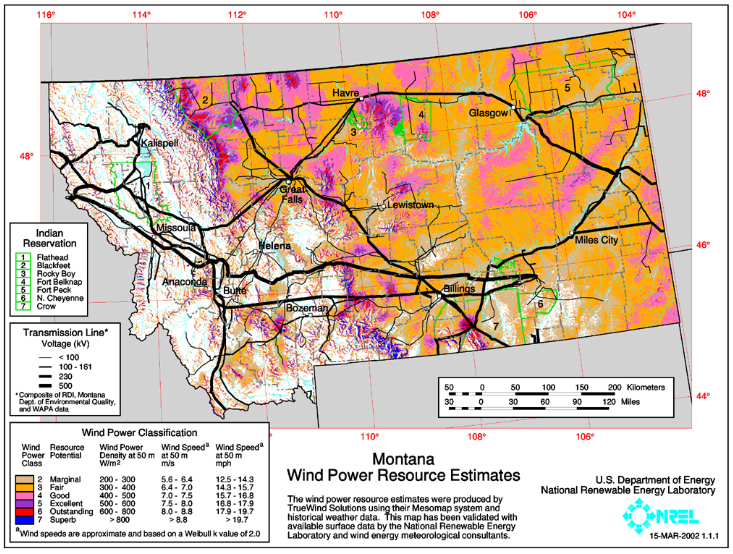
Blowin' in the wind . . .
This map shows
the best places in Montana to locate wind
generators. Montana is located in the wind
belt known as the westerlies, so winds
generally blow from west to east across the
state.
However, wind speeds and frequencies vary
greatly throughout the state due to variations
in the shape of the land. For instance,
mountains interrupt the westerly flow,
funneling the air through passes and down
valleys.  Red means windy . . . Red means windy . . .
On the map, those areas that are
purple, red, or blue have the best potential for
generating electricity. The blue areas are
considered to have the best (superb)
potential, the red areas have "outstanding"
potential, and the purple areas are considered
to be "excellent' locations. The larger, red
area in northwestern Montana marks the windy Rocky Mountain Front where the mountains
abruptly end, giving way to the plains. However, not every windy place is a good place for putting up wind-generators. For instance, "the Front" is valued for its scenic beauty and wildness, so there would be strong resistance to any proposal to place generators there.
Getting the product to market . . .
One of the most important considerations when selecting a site for placement of wind-generators is the location of transmission lines. The black lines on the map mark the location of major transmission lines in Montana. It is much easier and much less expensive to place wind-generators in close to transmission lines that can deliver the electricity to cities that need the power.
Sources of electricity . . .
According to experts, Montana ranks fifth
among states for wind power potential (USA wind map). So, as
a result of electricity shortages in recent years,
power companies have started taking steps to
develop Montana's wind resources. Most of
Montana's electricity comes from two sources.
The biggest portion is generated at coal-fired
plants such as those located in Colstrip.
Another source is hydro-power, which
originates at dams throughout the Northwest.
Perhaps the biggest benefit that
wind-generated electricity has over
coal-generated electricity is that
wind-generators do not produce any
emissions. This is important because most
scientists think that carbon dioxide from the
burning of coal is contributing to global
warming. On the other hand, some argue that
large numbers of wind generators would
damage the natural beauty of Montana
landscapes.
How do we "generate" electricity? . . .
Basically you need three things: a
magnet, a wire, and motion. If you were to
take a magnet and move it in close proximity
to a wire, you would cause an electrical
current to flow within the wire. Within a
generator, wires and magnets are organized
so that a current will be produced in the wires
if motion is provided. Generators can be
designed to utilize all sorts of motion ranging
from the peddling motion of a bicycle to the
motion of water through the bottom of a dam.
At coal-fired plants, coal is burned to heat
water. As the water changes to steam it
shoots through a turbine, providing the
motion. With wind generators, the wind turns
propeller-shaped turbines to generate
electricity. CLICK HERE to watch a YouTube video that shows how wind can cause electricity. Right: This photo by David Grubbs (courtesy of the Billings Gazette) shows a man standing on one of the wind turbines recently erected in central Montana (near Judith Gap). To learn more about this wind energy project, click on the Hot Link below.
Term: generator
|






